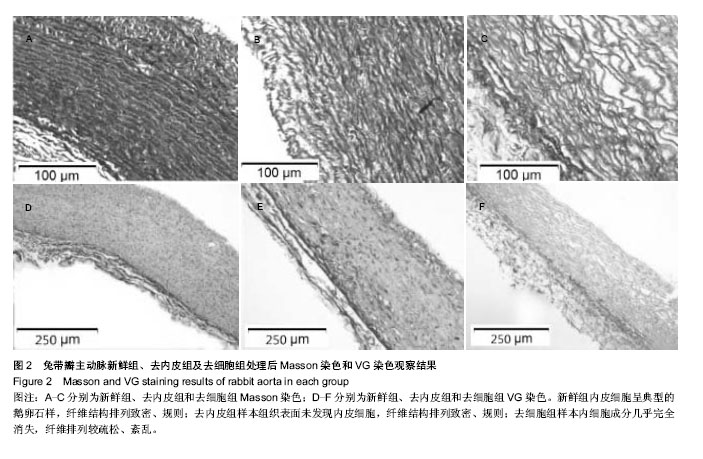
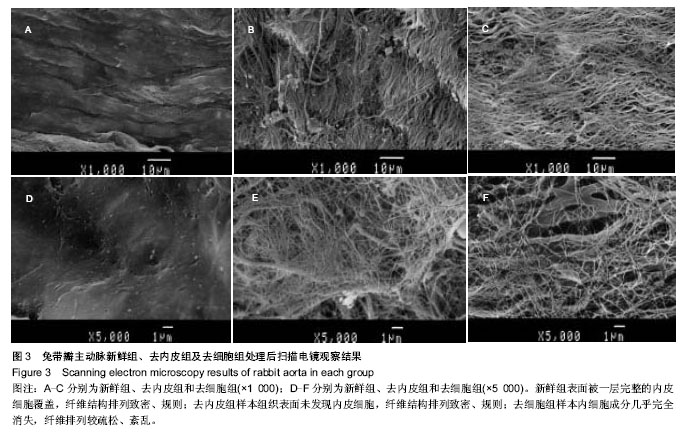
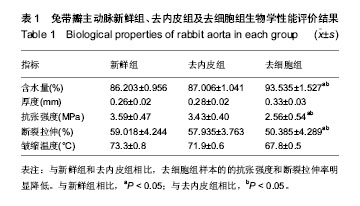
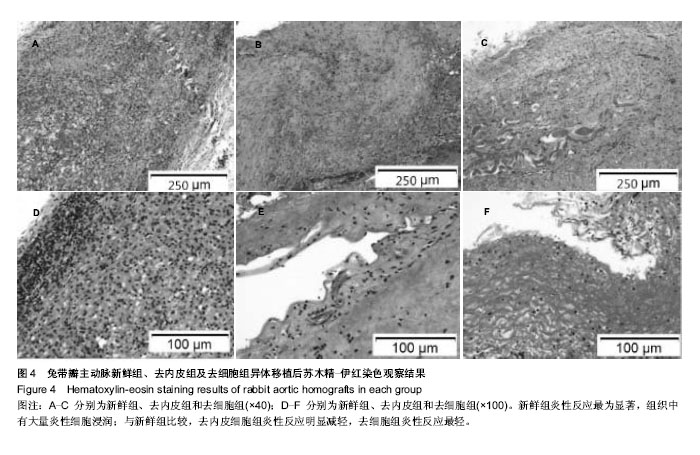
| [1]Musci M, Weng Y, Hübler M, et al.Homograft aortic root replacement in native or prosthetic active infective endocarditis: twenty-year single-center experience. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2010;139 (3):665-673.
[2]王盛宇,薛金熔,赵铁夫,等.同种主动脉瓣在心脏外科的应用[J].中国心血管病研究杂志, 2010,8(1):7-9.
[3]Kilian E, Fries F, Kowert A, et al.Homograft implantation for aortic valve replacement since 15 years: results and follow-up, Heart. Surg Forum. 2010;13(4):238-242.
[4]Vohra HA, Whistance RN, Chia AX, et al.Long-term follow-up after primary complete repair of common arterial trunk with homograft: a 40-year experience. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2010;140(2):325-329.
[5]da Costa FD, Costa AC, Prestes R,et al.The early and midterm function of decellularized aortic valve allografts. The Annals of thoracic surgery.2010;90(6):1854-1860.
[6]Kitamura S, Yagihara T, Kobayashi J, et al. Mid-to long-term outcomes of cardiovascular tissue replacements utilizing homografts harvested and stored at Japanese institutional tissue banks. Surgery today.2011;41(4):500-509.
[7]Park S, Hwang HY, Kim KH,et al.Midterm Follow-up after Cryopreserved Homograft Replacement in the Aortic Position. Korean J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2012;45(1):30-34.
[8]常青,李守先, 徐平,等.同种异体大鼠的主动脉移植后影响移植物钙化的因素分析[J].细胞与分子免疫学杂志, 2006, 22(1): 106-109.
[9]Kitamura S, Yagihara T, Kobayashi J, et al. Mid-to long-term outcomes of cardiovascular tissue replacements utilizing homografts harvested and stored at Japanese institutional tissue banks. Surgery today.2011;41(4): 500-509.
[10]Muratov R, Britikov D, Sachkov A, et al.New approach to reduce allograft tissue immunogenicity. Experimental data. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2010;10(3):408-412.
[11]Yu BT, Li WT, Song BQ, et al. Comparative study of the Triton X-100-sodium deoxycholate method and detergent-enzymatic digestion method for decellularization of porcine aortic valves.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2013; 17(16):2179-2184.
[12]Dohmen PM.Tissue engineered aortic valve. HSR proceedings in intensive care & cardiovascular anesthesia. 2012;4(2):89.
[13]Moccia F, Tanzi F, Munaron L. Endothelial Remodelling and Intracellular Calcium Machinery. Curr Mol Med. 2014;14(4): 457-480..
[14]赵金超,易定华,魏旭峰,等.环氧氯丙烷对戊二醛鞣制的猪主动脉瓣防钙化化学改性的实验研究[J].中国实用医药, 2008,3(6): 1-3.
[15]Chang Q, Jing H, Sun M, et al. Exploring the role of short-course cyclosporin a therapy in preventing homograft valve calcification after transplantation. Cellular immunology. 2014;287(1): 36-45.
[16]den Hamer I, Hepkema B, Prop J, et al.Hla antibodies specific for cryopreserved heart valve ‘‘homografts’’ in children. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1997;113 (2):417-419.
[17]Hoekstra F, Knoop C, Vaessen L, et al.Donor-specific cellular immune response against human cardiac valve allografts. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg.1996;112(2):281-286.
[18]Muratov R, Britikov D, Sachkov A, et al.New approach to reduce allograft tissue immunogenicity. Experimental data, Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac Surg. 2010;10(3):408-412.
[19]Kneib C, von Glehn CQ, Costa FD, et al.Evaluation of humoral immune response to donor HLA after implantation of cellularized versus decellularized human heart valve allografts, Tissue Antigens.2012;80(2):165-174.
[20]Lehr EJ, Rayat GR, Chiu B, et al.Decellularization reduces immunogenicity of sheep pulmonary artery vascular patches. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2011;141(4):1056-1062.
[21]Brockbank KG, Song YC.Mechanisms of bioprosthetic heart valve calcification1. Transplantation. 2003;75(8): 1133-1135.
[22]Taflin C, Charron D, Glotz D, et al.Immunological function of the endothelial cell within the setting of organ transplantation. Immunol Lett. 2011;139(1):1-6.
[23]Post IC, Weenink RP, van Wijk AC, et al.Characterization and quantification of porcine circulating endothelial cells. Xenotransplantation.2013;20(1):18-26.
[24]Wallbrecht K, Drick N, Hund AC, et al.Downregulation of endothelial adhesion molecules by dimethylfumarate, but not monomethylfumarate, and impairment of dynamic lymphocyte-endothelial cell interactions. Exp Dermatol. 2011; 20(12):980-985.
[25]Ferrero MC, Bregante J, Delpino M, et al.Proinflammatory response of human endothelial cells to Brucella infection, Microbes Infect. 2011;13(10):852-861.
[26]Kaveh M, Chayjan RA. Prediction of some physical and drying properties of terebinth fruit (pistacia atlantica l.) using artificial neural networks.Acta Sci Pol Technol Aliment.2014; 13(1):65-78.
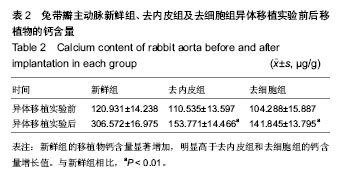
[27]巩性军,李守先,庞昕焱,等.同种带瓣主动脉移植后影响供体组织钙含量的相关性研究[J].中华实验外科杂志, 2009,26(3): 339-341.
[28]Zou W.Regulatory T cells,tumour immunity and immunotherapy.Nat Rev Immunol. 2006;6(4):295-307.
[29]Schweizer MT, Drake CG.Immunotherapy for prostate cancer: recent developments and future challenges.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2014 Jan 30. [Epub ahead of print].
[30]Kloog Y, Mor A. Cytotoxic-T-Lymphocyte Antigen 4 Receptor Signaling for Lymphocyte Adhesion Is Mediated by C3G and Rap1.Mol Cell Biol. 2014 ;34(6):978-988. |